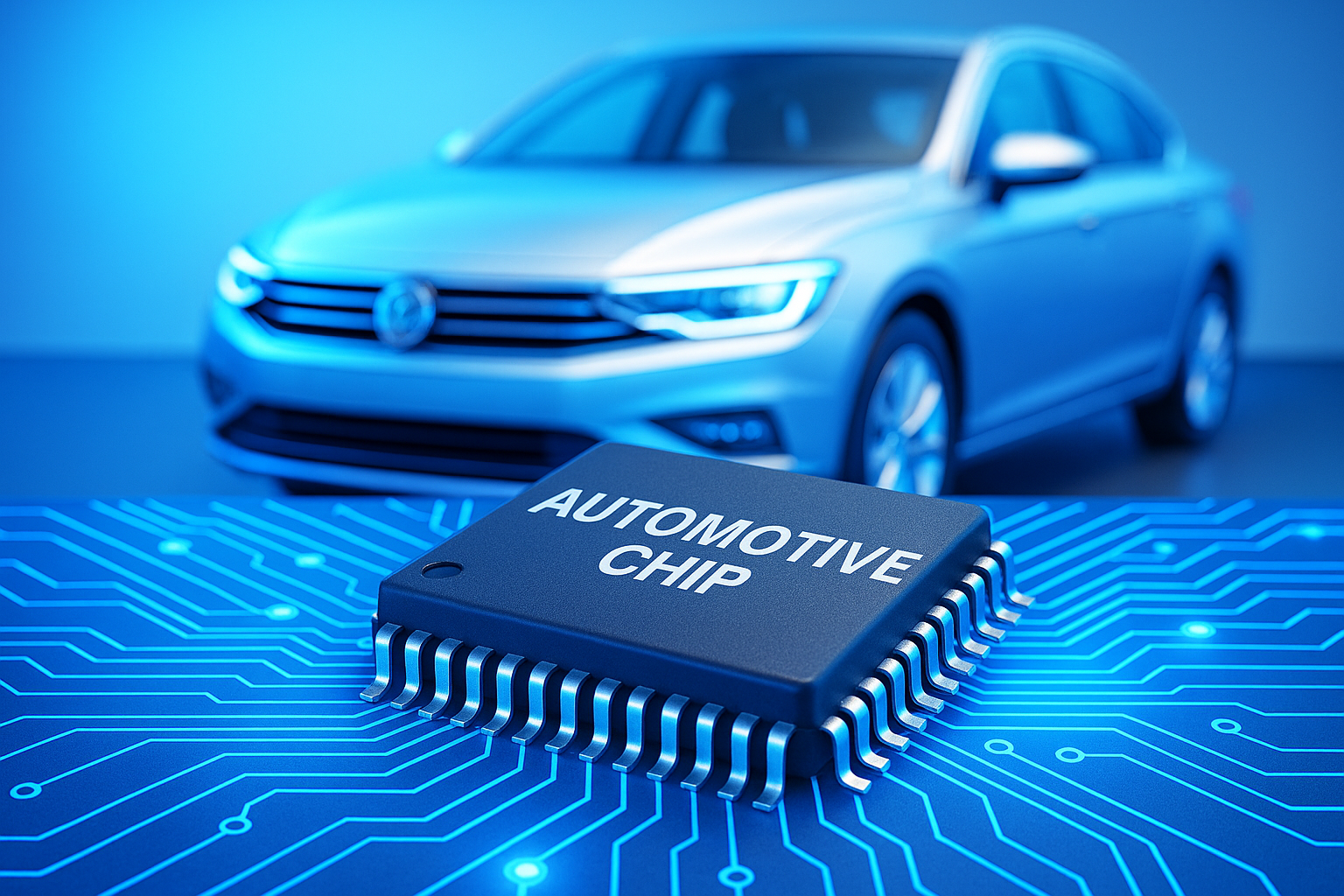
Recently, a statement by Audi’s Deputy General Manager Li Fenggang sparked a heated discussion in the tech community. He emphasized that automotive-grade and consumer-grade chips are fundamentally different, asserting:
"Audi would never test on its users—cars are not fast-moving consumer goods."
So, who is testing on users?
Chip Classifications Are Built on Risk, Not Price
As chip distributors, we interact daily with a wide spectrum of chips—from consumer electronics to aerospace-grade components. Each chip is designed for a unique operating environment, and the classification is never arbitrary.
Chip grading—from consumer-grade to aerospace-grade—is based on environmental stress, lifecycle expectations, defect tolerance, and safety risk. A smartphone crash might need a reboot. A car system failure could cost lives. In space, a chip error might cost billions.
This is why chip classification is not just a technical label—it is a risk management framework.

Five Levels of Chip Reliability: From Cost-Efficient to Mission-Critical
1. Consumer-Grade Chips: Optimized for Cost and Speed
Applications: Smartphones, tablets, home appliances
Temperature Range: 0°C to 70°C
Lifespan: 1–3 years
Defect Rate: ~500 PPM
Consumer chips prioritize low cost and rapid iteration. While suitable for mass-market devices, they are not built for long-term operation or extreme conditions. Testing standards are relatively loose, focusing on functionality rather than durability.
2. Industrial-Grade Chips: Designed for Harsh Environments
Applications: Automation, power systems, rail transit
Temperature Range: -40°C to +85°C (or higher)
Lifespan: 10+ years
Defect Rate: <50 PPM
Industrial chips are built for stability, often with robust packaging, extended temperature tolerance, and resistance to humidity, dust, and vibration. Certification processes include EMC, UL, and CE standards.
3. Automotive-Grade Chips: Safety First, Zero Compromise
Applications: ECUs, ADAS, engine control, automotive infotainment
Temperature Range: -40°C to +125°C
Defect Rate: <1 PPM
Certifications: AEC-Q100, ISO 26262
Automotive chips demand the highest levels of functional safety and reliability. Testing includes 1,000 hours at 85°C, 500 thermal cycles from -55°C to +125°C, and EMI/EMC resilience. Manufacturers like Audi require 10+ years of stable supply and multiple validation cycles.
4. Military-Grade Chips: Built for the Battlefield
Applications: Missiles, tanks, radar systems
Temperature Range: -55°C to +150°C
Defect Rate: <1 PPM
Standards: MIL-STD-883
Military chips withstand extreme temperatures, shock, EMP attacks, and radiation. Packaging often involves ceramic or metal for ultimate protection. These chips must ensure zero failure in mission-critical conditions.
5. Aerospace-Grade Chips: The Ultimate Reliability Benchmark
Applications: Satellites, rockets, space probes
Environment: Vacuum, cosmic radiation, long mission duration
Defect Rate: Lower than military-grade
Features: Radiation-hardening, SEU mitigation, custom shielding
Aerospace chips require years of qualification, extreme anti-radiation design, and “zero-maintenance” performance. A single fault in orbit is unacceptable. Some aerospace chips, like high-end radiation-hardened FPGAs, cost up to $500,000 per unit.
Chip Distribution Strategy by Grade: Tailored for Purpose
Consumer-Grade Strategy
Fast turnarounds: Sync with OEMs and ODMs for rapid design updates
Lean inventory: Small-batch, high-frequency stock to avoid obsolescence
Message: Focus on performance (5G, AI), avoid overpromising reliability
Industrial-Grade Strategy
Technical support: FAE teams for EMC, aging, and compliance assistance
Long-term contracts: Secure 10+ year lifecycle agreements
Customization: BOM optimization for voltage range, vibration resistance
Automotive-Grade Strategy
Certification readiness: Guide clients through AEC-Q100 and ISO standards
Supply chain resilience: Dual-sourcing to mitigate geopolitical risks
Hybrid cost control: Use consumer-grade in non-critical systems, car-grade in safety areas
Military-Grade Strategy
Compliance: EAR, ITAR export control screening
Localization: Support domestic replacements with full verification
Readiness: Strategic stockpiling for emergency demand
Final Word: Chip Classification Is a Responsibility Chain
Chip classification isn't about marketing tiers—it's about life-and-death reliability.
Each grade serves a purpose. Misapplying them is more than a technical error; it's a risk decision that can cost lives, reputations, or billions in damage.
As a chip distributor, understanding and respecting these distinctions is not only our value, but our duty.


 MCU Solutions
MCU Solutions PCBA Solutions
PCBA Solutions Bluetooth Solutions
Bluetooth Solutions
 FAQ
FAQ Contact Us
Contact Us
 Company News
Company News Technology News
Technology News Industry News
Industry News PCBA News
PCBA News
 Company Profile
Company Profile Certificates
Certificates Terms & Conditions
Terms & Conditions Privacy Statement
Privacy Statement
 Home Appliances
Home Appliances Beauty Appliances
Beauty Appliances Lighting
Lighting Kid's Toys
Kid's Toys Security Alarm
Security Alarm Health Care
Health Care



 More information?
More information?






